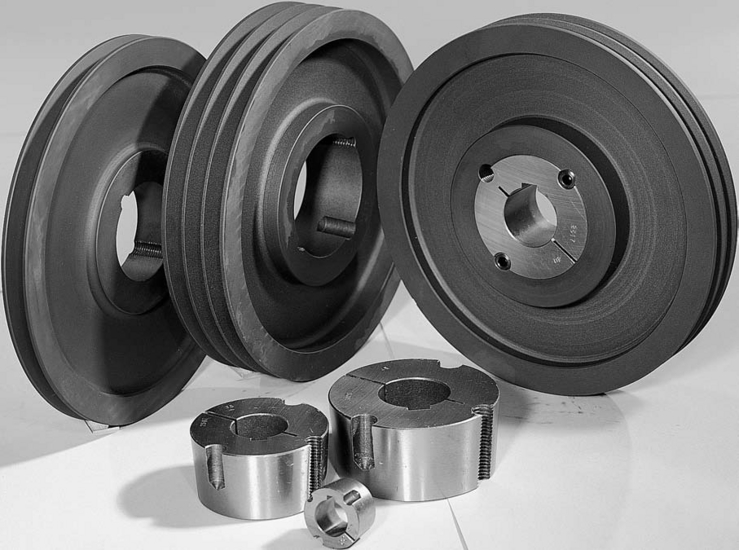
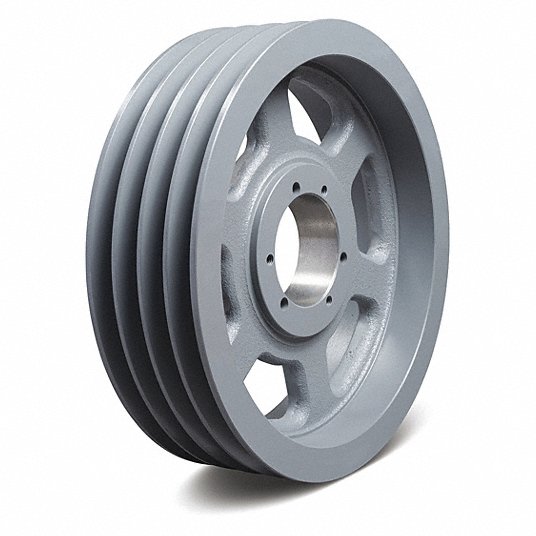
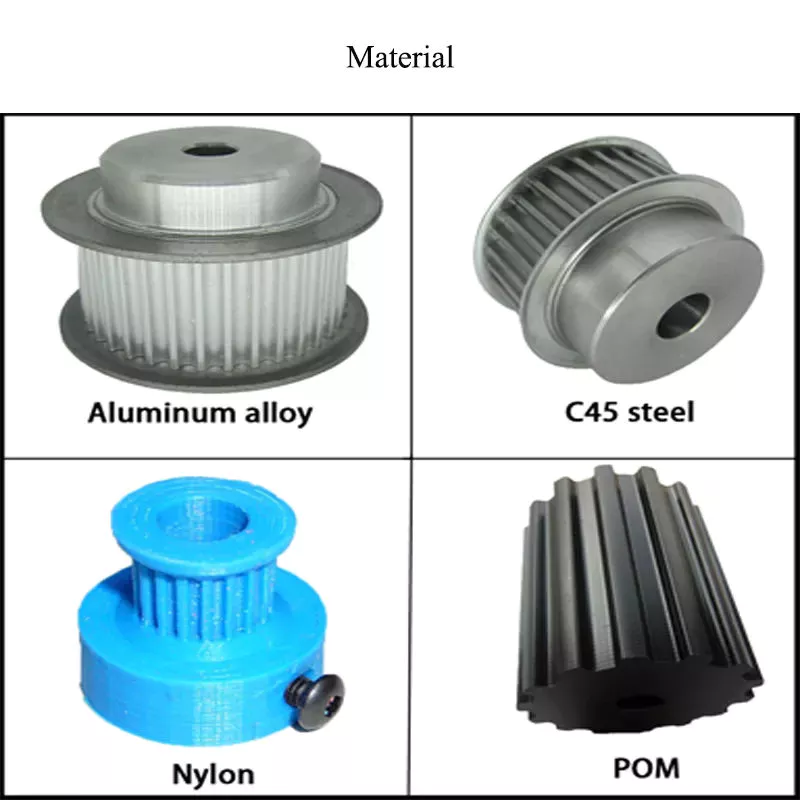
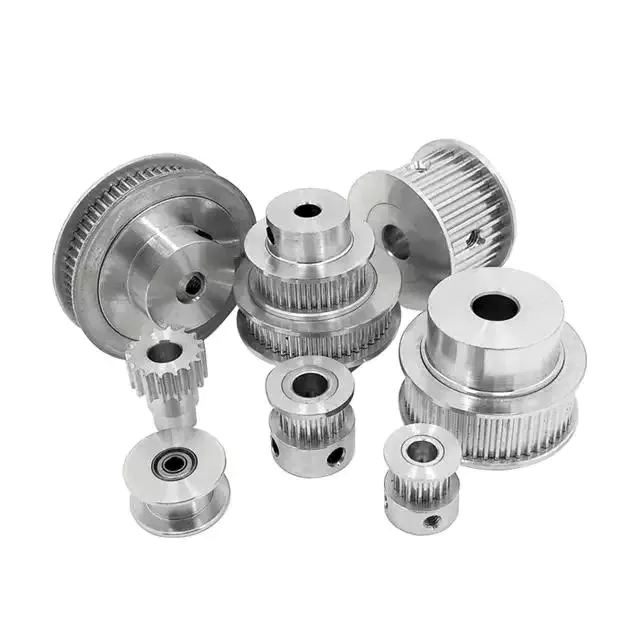
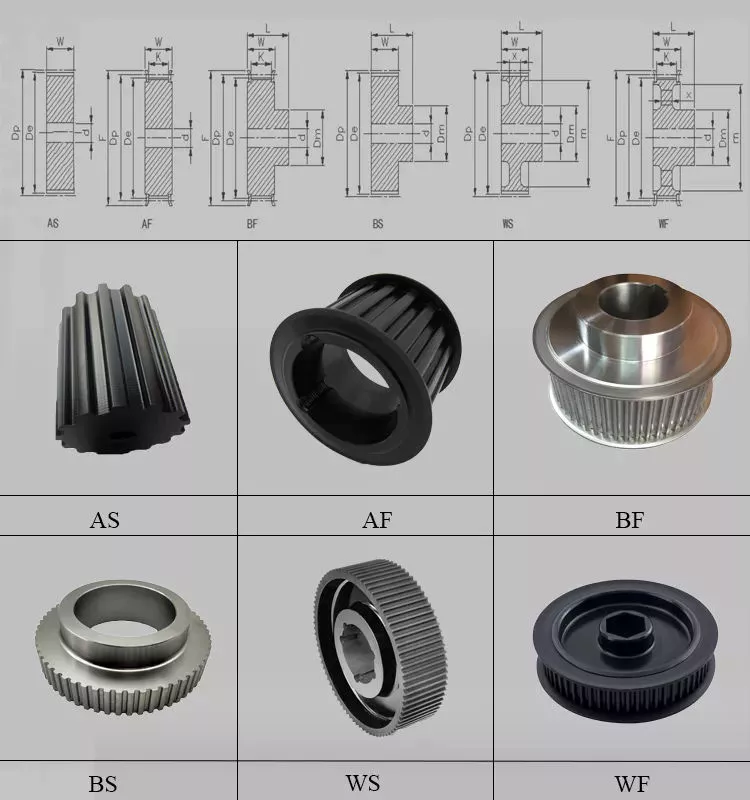
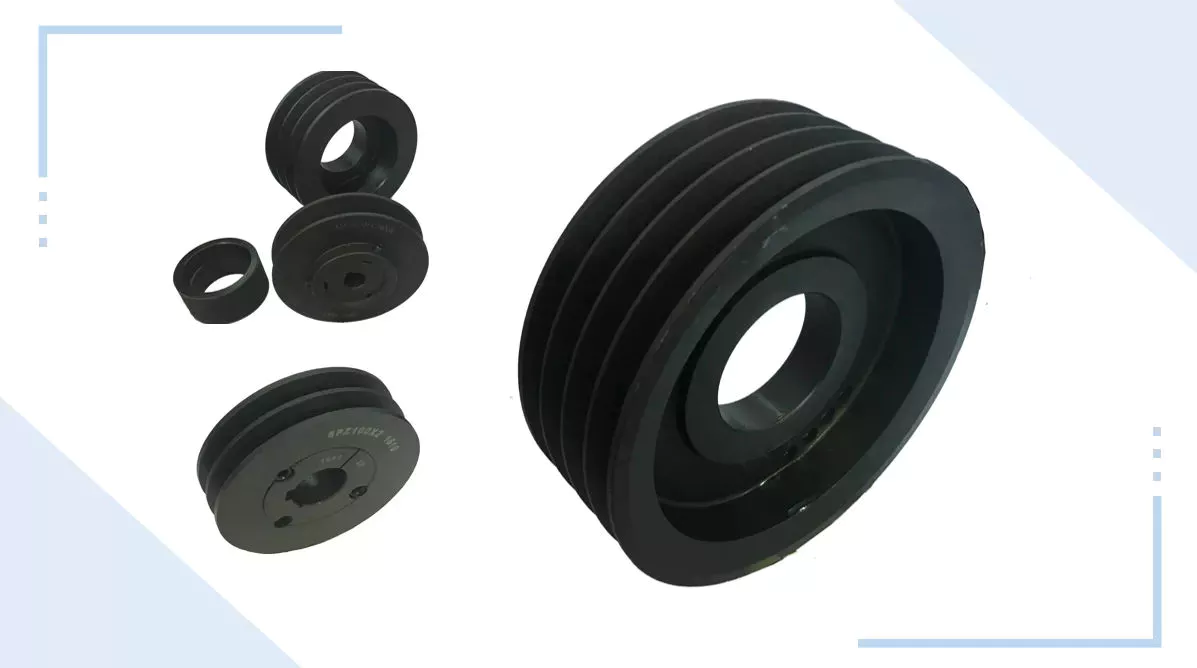
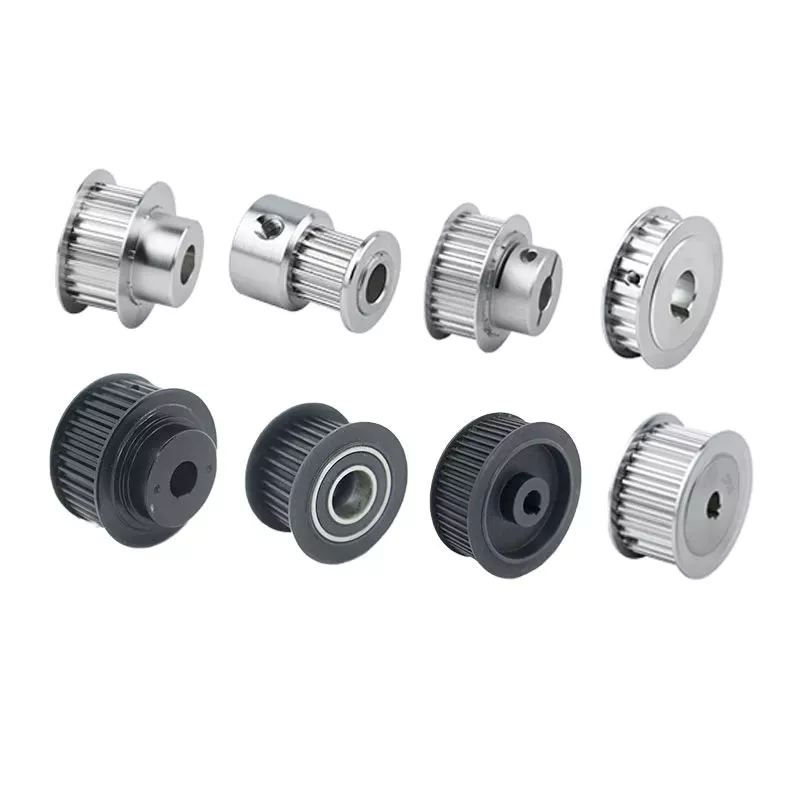
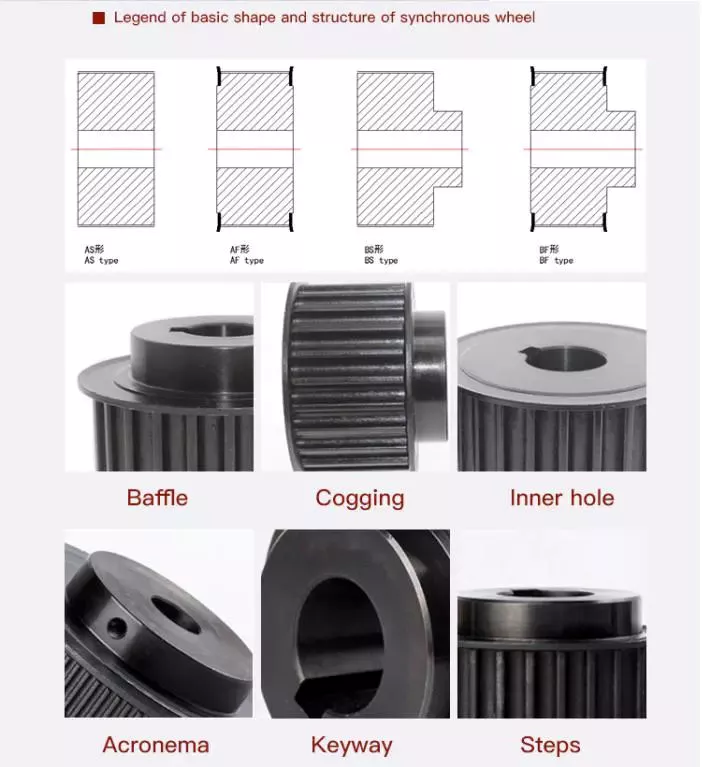
Product Description
Differential V-Belt Conveyor Toothed Idler Metric Gear Belt Drive Aluminium Tensioner Pitch Plastic Miniature Timing Pulley Manufacturers
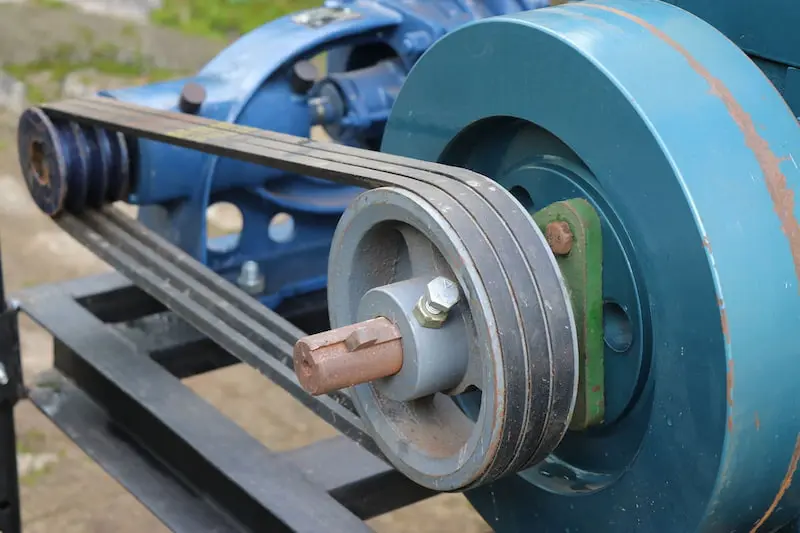
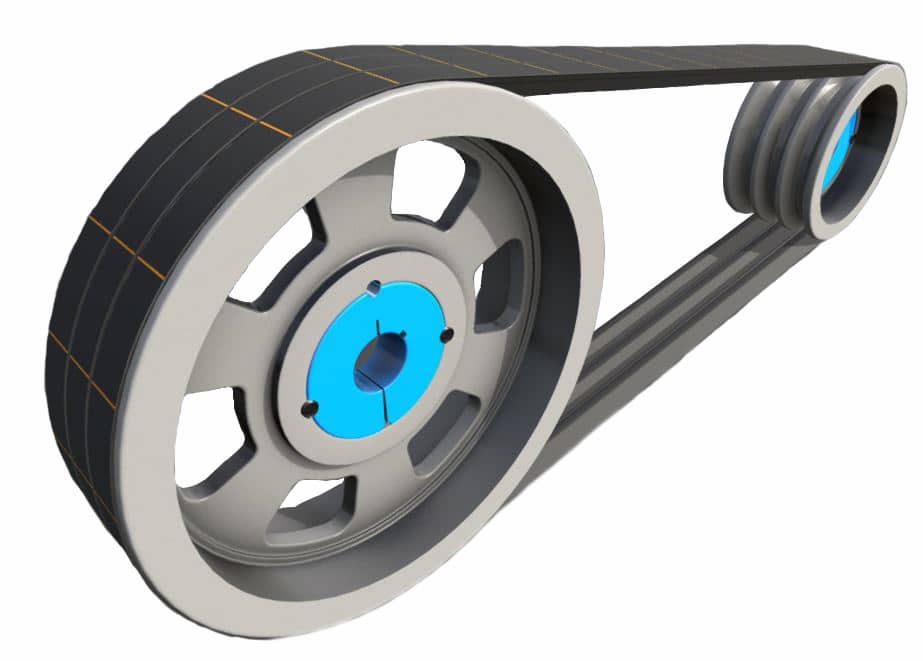
In power transmission, belts are flexible loops of material that can link 2 rotating shafts mechanically and transmit power between them. Belts are also the primary component in belt drives, where 1 or more continuous belts are fitted over 2 pulleys at 2 shafts and rotary motion is transferred from the driving pulley to the driven pulley.
As compared to chain drives and gear drives, belt drives run quietly and smoothly and do not need lubrication. Maintenance is also comparatively convenient, and the driven shaft speed can be easily altered by changing pulley sizes.
The most common types of belts are V-belts and timing belts. V-belts are the most common type of belt today, and as their name suggests, their cross-sectional shape comes in the form of a “V”. Generally endless, the “V” cross-sections of these belts lodge in the mating grooves of their corresponding V-belt pulleys, preventing slipping due to under-10sioning. In general, V-belts require less width and tension compared to flat belts.
Timing belts are toothed belts that enable positive drive. They have rows of interlocking teeth that fit securely with a toothed pulley to avoid slipping. Timing belts require less tension than other belts, have no slippage, and do not require lubrication, however their power capacity is lower than V-belts and chains. They are frequently used in camshafts of automobiles and crankshafts.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Certification: | CE, ISO |
|---|---|
| Pulley Sizes: | V-Belt Pulley SPA/06 |
| Manufacturing Process: | Casting |
| Material: | Iron |
| Surface Treatment: | Phosphating |
| Application: | Chemical Industry, Grain Transport, Mining Transport, Power Plant |
| Samples: |
US$ 9999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What is the significance of proper alignment in gear pulley systems?
Proper alignment in gear pulley systems is of significant importance for ensuring optimal performance, efficiency, and longevity of the system. Here’s a detailed explanation of the significance of proper alignment in gear pulley systems:
1. Efficient Power Transmission:
Proper alignment ensures that the gears and pulleys engage correctly, resulting in efficient power transmission. Misalignment can cause excessive friction, energy loss, and premature wear of components. When the gears and pulleys are properly aligned, the force is evenly distributed across the teeth and surfaces, minimizing energy losses and maximizing the transfer of rotational power from the driving gear to the driven gear or pulley.
2. Smooth Operation:
Alignment plays a crucial role in achieving smooth and vibration-free operation of gear pulley systems. Misalignment can lead to uneven forces and vibrations, causing noise, increased wear, and reduced system stability. Proper alignment ensures that the gears and pulleys rotate without excessive axial or radial movement, resulting in smooth and reliable operation.
3. Extended Component Life:
Proper alignment helps prolong the life of gears, pulleys, bearings, and other components in the system. Misalignment can create excessive stresses on the teeth, shafts, and bearings, leading to premature wear, pitting, or failure. By ensuring proper alignment, the load is evenly distributed, reducing stress concentrations and promoting longer component life.
4. Accurate Speed and Torque Transmission:
In gear pulley systems, accurate speed and torque transmission are crucial for achieving the desired performance. Misalignment can cause deviations in rotational speed and torque, leading to inaccurate operation and reduced system performance. Proper alignment ensures that the gears and pulleys maintain the intended contact and engagement, resulting in accurate speed and torque transmission.
5. Reduced Energy Consumption:
Misalignment in gear pulley systems can result in increased energy consumption. The inefficiencies caused by misalignment, such as friction and energy losses, require the system to consume more power to achieve the desired output. Proper alignment minimizes these inefficiencies, reducing energy consumption and improving overall system efficiency.
6. Preventive Maintenance:
Proper alignment is essential for preventive maintenance practices. Regular inspection and adjustment of alignment help identify and correct any misalignment issues before they lead to significant damage or system failure. By proactively maintaining proper alignment, potential problems can be addressed early, reducing downtime and repair costs.
7. Safety:
Proper alignment contributes to the safety of gear pulley systems. Misalignment can create unexpected forces, vibrations, or sudden movements, posing safety risks to operators and surrounding equipment. Properly aligned systems operate predictably and reliably, minimizing the risk of accidents or damage.
In summary, proper alignment in gear pulley systems is crucial for efficient power transmission, smooth operation, extended component life, accurate speed and torque transmission, reduced energy consumption, preventive maintenance, and safety. Regular inspection and adjustment of alignment are necessary to ensure optimal performance and reliability of gear pulley systems.

What safety considerations should be kept in mind when using gear pulleys?
When using gear pulleys, several safety considerations should be kept in mind to prevent accidents, ensure operator safety, and maintain equipment integrity. Here’s a detailed explanation of the safety considerations associated with gear pulley usage:
1. Guarding:
It is essential to have appropriate guarding in place to prevent accidental contact with rotating gear pulleys. Guards should be designed and installed to restrict access to the moving parts of the gear pulley system, minimizing the risk of entanglement, pinching, or crushing injuries. Guards should be securely attached and provide sufficient visibility for monitoring the operation while ensuring operator safety.
2. Lockout-Tagout (LOTO):
Proper lockout-tagout procedures should be followed when performing maintenance, repairs, or adjustments on gear pulley systems. LOTO procedures involve isolating the power source, locking the energy-isolating device, and tagging it to indicate that maintenance work is in progress. This precaution prevents unintended startup of the machinery, protecting personnel from potential hazards associated with gear pulley movement.
3. Training and Education:
Operators and maintenance personnel should receive comprehensive training on the safe operation, maintenance, and inspection of gear pulleys. They should be educated about the potential hazards, safety procedures, and proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Training should cover topics such as safe work practices, emergency procedures, hazard identification, and reporting of any malfunctions or abnormalities.
4. PPE (Personal Protective Equipment):
Appropriate personal protective equipment should be worn when working with or around gear pulleys. This may include safety glasses or goggles, protective gloves, hearing protection, and, depending on the application, protective clothing such as helmets or safety shoes. PPE helps mitigate the risk of injuries from flying debris, noise exposure, or contact with rotating parts.
5. Regular Inspection and Maintenance:
Gear pulleys should undergo regular inspection and maintenance to ensure proper functioning and identify any potential safety hazards. This includes checking for worn or damaged gears, loose fasteners, misalignment, excessive vibration, or signs of lubrication issues. Any abnormalities should be promptly addressed to prevent equipment failure or accidents during operation.
6. Load Capacities and Ratings:
It is crucial to adhere to the load capacities and ratings specified by the gear pulley manufacturer. Overloading the gear pulley system can lead to excessive stress, premature failure, or catastrophic accidents. Operators should be aware of the system’s maximum load capacity and ensure that it is not exceeded during operation.
7. Proper Installation and Alignment:
Gear pulleys should be installed and aligned correctly to prevent excessive wear, noise, or premature failure. Proper alignment ensures smooth operation and minimizes the risk of unexpected movements or disengagement. It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for installation, alignment, and adjustment of gear pulleys to maintain safe and reliable operation.
8. Hazardous Environments:
In certain industrial environments, gear pulleys may be exposed to hazardous substances, extreme temperatures, or corrosive materials. It is important to consider the specific hazards of the working environment and select gear pulleys that are suitable for those conditions. Additional safety measures, such as protective coatings, ventilation systems, or specialized gear materials, may be required to ensure safe operation in such environments.
9. Proper Handling and Lifting:
When handling gear pulleys, proper lifting techniques should be employed to avoid strain or injuries. If gear pulleys are large or heavy, appropriate lifting equipment or machinery should be used. Operators should be trained in safe lifting practices and ensure that they have a clear path and adequate space when moving or positioning gear pulleys.
10. Emergency Stop and Warning Systems:
Gear pulley systems should be equipped with emergency stop mechanisms and clearly visible warning signs or labels. Emergency stops allow operators to quickly halt the machinery in case of an emergency or imminent danger. Warning signs or labels should provide clear instructions, cautions, and safety information to alert personnel about potential hazards associated with gear pulley operation.
In summary, the safety considerations when using gear pulleys include proper guarding, adherence to lockout-tagout procedures, adequate training and education, use of personal protective equipment, regular inspection and maintenance, adherence to load capacities and ratings, proper installation and alignment, awareness of hazardous environments, safe handling and lifting practices, and the presence of emergency stop and warning systems. By implementing these safety measures, the risk of accidents and injuries associated
What safety considerations should be kept in mind when using gear pulleys?
When using gear pulleys, several safety considerations should be kept in mind to prevent accidents, ensure operator safety, and maintain equipment integrity. Here’s a detailed explanation of the safety considerations associated with gear pulley usage:
- Guarding: It is essential to have appropriate guarding in place to prevent accidental contact with rotating gear pulleys. Guards should be designed and installed to restrict access to the moving parts of the gear pulley system, minimizing the risk of entanglement, pinching, or crushing injuries. Guards should be securely attached and provide sufficient visibility for monitoring the operation while ensuring operator safety.
- Lockout-Tagout (LOTO): Proper lockout-tagout procedures should be followed when performing maintenance, repairs, or adjustments on gear pulley systems. LOTO procedures involve isolating the power source, locking the energy-isolating device, and tagging it to indicate that maintenance work is in progress. This precaution prevents unintended startup of the machinery, protecting personnel from potential hazards associated with gear pulley movement.
- Training and Education: Operators and maintenance personnel should receive comprehensive training on the safe operation, maintenance, and inspection of gear pulleys. They should be educated about the potential hazards, safety procedures, and proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Training should cover topics such as safe work practices, emergency procedures, hazard identification, and reporting of any malfunctions or abnormalities.
- PPE (Personal Protective Equipment): Appropriate personal protective equipment should be worn when working with or around gear pulleys. This may include safety glasses or goggles, protective gloves, hearing protection, and, depending on the application, protective clothing such as helmets or safety shoes. PPE helps mitigate the risk of injuries from flying debris, noise exposure, or contact with rotating parts.
- Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Gear pulleys should undergo regular inspection and maintenance to ensure proper functioning and identify any potential safety hazards. This includes checking for worn or damaged gears, loose fasteners, misalignment, excessive vibration, or signs of lubrication issues. Any abnormalities should be promptly addressed to prevent equipment failure or accidents during operation.
- Load Capacities and Ratings: It is crucial to adhere to the load capacities and ratings specified by the gear pulley manufacturer. Overloading the gear pulley system can lead to excessive stress, premature failure, or catastrophic accidents. Operators should be aware of the system’s maximum load capacity and ensure that it is not exceeded during operation.
- Proper Installation and Alignment: Gear pulleys should be installed and aligned correctly to prevent excessive wear, noise, or premature failure. Proper alignment ensures smooth operation and minimizes the risk of unexpected movements or disengagement. It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for installation, alignment, and adjustment of gear pulleys to maintain safe and reliable operation.
- Hazardous Environments: In certain industrial environments, gear pulleys may be exposed to hazardous substances, extreme temperatures, or corrosive materials. It is important to consider the specific hazards of the working environment and select gear pulleys that are suitable for those conditions. Additional safety measures, such as protective coatings, ventilation systems, or specialized gear materials, may be required to ensure safe operation in such environments.
- Proper Handling and Lifting: When handling gear pulleys, proper lifting techniques should be employed to avoid strain or injuries. If gear pulleys are large or heavy, appropriate lifting equipment or machinery should be used. Operators should be trained in safe lifting practices and ensure that they have a clear path and adequate space when moving or positioning gear pulleys.
- Emergency Stop and Warning Systems: Gear pulley systems should be equipped with emergency stop mechanisms and clearly visible warning signs or labels. Emergency stops allow operators to quickly halt the machinery in case of an emergency or imminent danger. Warning signs or labels should provide clear instructions, cautions, and safety information to alert personnel about potential hazards associated with gear pulley operation.
In summary, the safety considerations when using gear pulleys include proper guarding, adherence to lockout-tagout procedures, adequate training and education, use of personal protective equipment, regular inspection and maintenance, adherence to load capacities and ratings, proper installation and alignment, awareness of hazardous environments, safe handling and lifting practices, and the presence of emergency stop and warning systems. By implementing these safety measures, the risk of accidents and injuries associated with gear pulley usage can be minimized, promoting a safe working environment.

What is a gear pulley, and how does it function in mechanical systems?
A gear pulley, also known as a gear and pulley system, combines the functionality of gears and pulleys to transmit power and control the speed and torque in mechanical systems. Here’s an explanation of what a gear pulley is and how it functions:
A gear pulley is a mechanical system that consists of two or more gears and one or more pulleys connected together. Gears are toothed wheels that mesh together to transmit rotational motion and torque, while pulleys are grooved wheels that use a belt or a rope to transmit motion and force. By combining these two components, a gear pulley system can achieve various mechanical advantages and control the speed and torque of the system.
The functioning of a gear pulley system can be understood through the following key points:
- Power Transmission: The primary function of a gear pulley system is to transmit power from one component to another. When the input gear or pulley is rotated, it causes the corresponding output gear or pulley to rotate as well. This rotation transfers power from the input to the output, allowing the system to perform work. The gears and pulleys enable the power to be transmitted efficiently and effectively across the system.
- Mechanical Advantage: Gear pulley systems provide mechanical advantage, allowing for the amplification or reduction of force and torque. Gears, with their different sizes and number of teeth, can change the rotational speed and torque of the system. By selecting gears with different ratios, the gear pulley system can increase the torque output while reducing the rotational speed (increased force, decreased speed) or increase the rotational speed while reducing the torque output (decreased force, increased speed).
- Speed Control: One of the key functions of a gear pulley system is speed control. By using gears with different sizes, the system can adjust the speed at which the output component rotates. Larger gears will result in slower output speed, while smaller gears will result in faster output speed. This feature is especially useful in applications where precise speed control is required, such as in machinery and automotive systems.
- Direction Control: The arrangement of gears and pulleys in a gear pulley system can also control the direction of rotation. By using various gear configurations, such as spur gears, bevel gears, or worm gears, the system can achieve different rotational directions. This allows for versatile control and manipulation of the mechanical system based on the desired outcome.
- Tension and Belt Control: In gear pulley systems that incorporate belts or ropes, the pulleys play a crucial role in maintaining tension and controlling the movement of the belts. The grooves on the pulleys ensure that the belts remain in place and transmit force efficiently. By adjusting the size and position of the pulleys, the tension in the belts can be controlled, ensuring smooth operation and reducing slippage.
- Transfer of Motion: A gear pulley system can transfer motion and power between non-parallel shafts, allowing for flexibility in mechanical designs. By using appropriate gears and pulleys, the system can change the direction of rotation, transfer motion at different angles, and transmit power between components that are not directly in line with each other. This versatility expands the range of applications where gear pulley systems can be employed.
In summary, a gear pulley system combines gears and pulleys to transmit power, control speed and torque, and achieve mechanical advantages in mechanical systems. By selecting appropriate gear ratios, sizes, and configurations, gear pulley systems provide efficient power transmission, speed control, direction control, tension control, and the transfer of motion in a wide range of applications.


editor by CX
2024-04-29