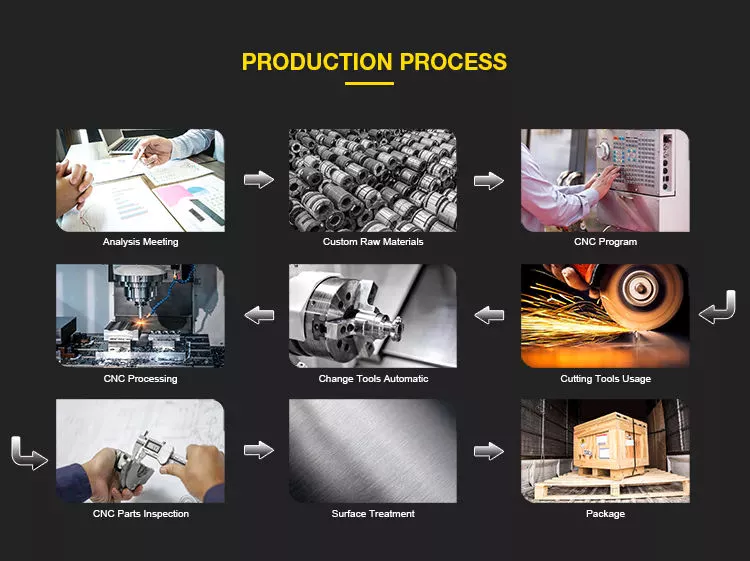
Product Description
Our Advantages
-
Highly customized, minimum order accept 1 roller.
Price favorable.
Delivery time is faster and more flexible!
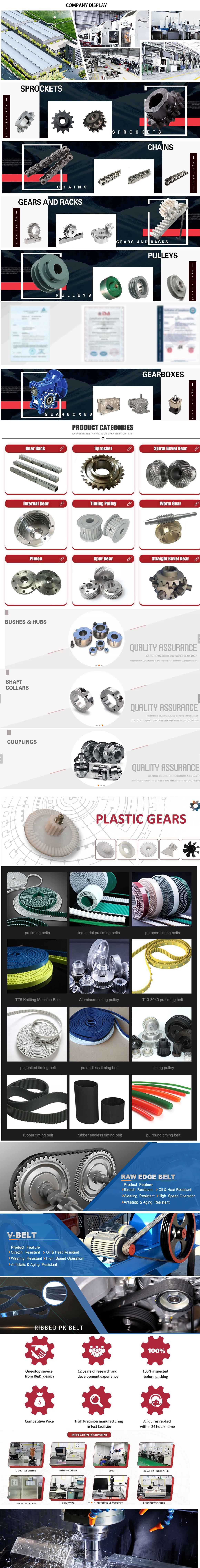
Company Profile
Certifications
FAQ
Q: What’re your main products?
A: DC brushless motor roller/AC 3ph motor roller/Direct drive motor roller/Oil immersed motor roller/Gear reduction motor/controller box
Q: How to select a suitable motor roller?
A:If you have motor roller pictures or drawings to show us, or you have detailed specs like conveyor mode(pallet or belt),linear speed,loading weight,loading object material,roller diameter,length,voltage and noise level etc, then we can recommend suitable motor roller to you.
Q: Do you have a customized service for your standard motor rollers?
A: Yes, we can customize.
Q: Do you have an individual design service for motor rollers?
A: Yes, we would like to design roller individually for our customers.
Q: What’s your lead time?
A: Generally speaking, our regular standard product will need 7~15days, a bit longer for customized products. But we are very flexible on the lead time, it will depend on the specific orders.
Product Description
Detailed Photos
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|
| Surface Treatment: | Electroplating |
| Motor Type: | Build-in Motor |
| Installation: | Horizontal |
| Rated Speed: | 1m/Min~95.4m/Min |
| Rated Power: | 40W/80W |
| Samples: |
US$ 200/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What maintenance procedures are necessary to ensure the reliability of gear pulleys?
Proper maintenance procedures are crucial for ensuring the reliability and longevity of gear pulleys. Here are some essential maintenance steps to consider:
- Regular Inspection: Conduct routine inspections of the gear pulleys to check for any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Inspect the gear teeth, pulley surfaces, and the overall condition of the pulley assembly. Look for any cracks, chips, or excessive wear that may affect the pulley’s performance.
- Lubrication: Ensure that the gear pulleys are adequately lubricated. Lubrication helps reduce friction and wear between the gear teeth and the pulley surfaces. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the appropriate lubricant type and schedule. Apply lubrication as specified to maintain smooth operation and prevent premature failure.
- Tension Adjustment: Check the tension of the belt connected to the gear pulleys. Proper tension is essential for efficient power transmission and to prevent slippage. If the belt is too loose or too tight, adjust the tension according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Use tensioning devices such as idler pulleys or tensioners to achieve the optimal tension.
- Alignment: Ensure that the gear pulleys are properly aligned. Misalignment can lead to excessive wear, noise, and reduced efficiency. Use alignment tools and techniques to align the pulleys accurately. Check the alignment periodically and make any necessary adjustments to maintain proper alignment.
- Cleaning: Keep the gear pulleys clean and free from dirt, debris, and contaminants. Regularly clean the pulley surfaces using a suitable cleaning method recommended by the manufacturer. This helps prevent abrasive particles from damaging the gear teeth and ensures smooth operation.
- Replacement: If any significant wear, damage, or defects are observed during inspection, consider replacing the gear pulleys promptly. Delaying the replacement can result in further damage to the pulleys and other system components. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and specifications for selecting and installing the appropriate replacement pulleys.
- Professional Maintenance: In complex HVAC systems or air conditioning units, it is often advisable to seek professional maintenance services. HVAC technicians or qualified professionals can perform comprehensive inspections, maintenance, and repairs on gear pulleys and associated components.
By following these maintenance procedures, you can ensure the reliability and optimal performance of gear pulleys in HVAC systems and air conditioning units. Regular inspections, lubrication, tension adjustment, alignment checks, cleaning, and timely replacement contribute to the longevity and efficiency of gear pulleys, minimizing the risk of unexpected failures and system downtime.

How does the gear ratio in a gear pulley affect its performance?
The gear ratio in a gear pulley has a significant impact on its performance, influencing various aspects such as speed, torque, and power transmission. Here’s a detailed explanation of how the gear ratio affects the performance of a gear pulley:
Gear Ratio Basics:
The gear ratio represents the relationship between the number of teeth on the driving gear and the number of teeth on the driven gear. It determines how many times the driving gear must rotate to make the driven gear complete one revolution. The gear ratio is typically expressed as a numerical ratio or as a fraction.
Speed:
The gear ratio directly affects the speed of the driven gear relative to the driving gear. A gear pulley with a higher gear ratio, where the driving gear has more teeth than the driven gear, will result in a lower speed at the driven gear. Conversely, a gear pulley with a lower gear ratio, where the driven gear has more teeth, will result in a higher speed at the driven gear. Therefore, the gear ratio determines the speed reduction or amplification between the driving and driven gears.
Torque:
The gear ratio also influences the torque at the driven gear. Torque is a rotational force that determines the system’s ability to overcome resistance or to perform work. A gear pulley with a higher gear ratio, where the driving gear has more teeth, will result in a torque amplification at the driven gear. This means that the driven gear can exert greater force or torque on the load or system it is connected to. Conversely, a gear pulley with a lower gear ratio, where the driven gear has more teeth, will result in a torque reduction at the driven gear. In this case, the driven gear will exert less force or torque, but it will be able to rotate at a higher speed.
Power Transmission:
The gear ratio affects the power transmission capabilities of the gear pulley system. Power is the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred. The gear ratio determines how the power is distributed between the driving and driven gears. In a gear pulley system, the power is equal to the product of torque and rotational speed. A higher gear ratio will result in a higher torque at the driven gear, allowing it to transmit more power to the connected system. Conversely, a lower gear ratio will result in a higher speed at the driven gear, enabling it to transmit power at a faster rate.
Mechanical Advantage:
The gear ratio provides mechanical advantage in a gear pulley system. Mechanical advantage refers to the ability of a system to amplify force or torque. A gear pulley with a higher gear ratio provides a greater mechanical advantage, allowing it to handle heavier loads or perform tasks that require more force. On the other hand, a gear pulley with a lower gear ratio provides a lower mechanical advantage but allows for higher speeds and faster operation.
Efficiency:
The gear ratio can also impact the overall efficiency of the gear pulley system. In general, gear systems with higher gear ratios tend to have lower efficiency due to increased friction and power losses. The additional teeth in the gear train result in more contact points and increased surface area, leading to higher friction losses. Therefore, it is important to consider the trade-off between speed, torque, and efficiency when selecting the gear ratio for a specific application.
Overall, the gear ratio in a gear pulley significantly affects its performance, including speed, torque, power transmission, mechanical advantage, and efficiency. By selecting the appropriate gear ratio, engineers and designers can optimize the gear pulley system for specific applications, ensuring the desired balance between speed, torque, and efficiency based on the requirements of the machinery or system.

How do gear pulleys assist in the transmission of mechanical power?
Gear pulleys play a crucial role in the transmission of mechanical power in various systems. Here’s an explanation of how gear pulleys assist in the transmission of mechanical power:
Gear pulleys are part of power transmission systems that transfer rotational motion and torque from a power source to a driven component. They achieve this by utilizing the principles of gears and pulleys to control speed, torque, and direction. The primary function of gear pulleys is to transmit power efficiently and effectively between rotating shafts.
Here are the key ways in which gear pulleys assist in the transmission of mechanical power:
- Speed Control: Gear pulleys allow for speed control in power transmission systems. By using gears with different sizes or pulleys with varying diameters, the rotational speed of the driven component can be adjusted relative to the input speed. Larger gears or pulleys connected to the power source result in higher speed reduction, while smaller gears or pulleys result in higher speed amplification. This speed control capability enables gear pulleys to match the rotational speed requirements of different components within a system.
- Torque Conversion: Gear pulleys assist in torque conversion during power transmission. Torque is the rotational force generated by the power source. By using gears or pulleys with different numbers of teeth or diameters, gear pulleys can change the torque applied to the driven component. In a gear system, when a larger gear drives a smaller gear, the torque is increased, enabling the transmission of higher rotational force. Conversely, when a smaller gear drives a larger gear, the torque is reduced. This torque conversion capability allows gear pulleys to adapt the power output to the requirements of the driven component.
- Direction Control: Gear pulleys enable the control of rotational direction in power transmission systems. By using gears or pulleys in combination with other components such as idler gears or reversing pulleys, the direction of rotation can be changed. For example, meshing two gears in a gear system can transmit power in the same or opposite directions depending on their arrangement. Similarly, using pulleys with different groove orientations can alter the direction of belt-driven power transmission. This direction control capability allows gear pulleys to accommodate the specific needs of different components within a system.
- Power Distribution: Gear pulleys assist in the distribution of mechanical power to multiple driven components. By incorporating multiple gears or pulleys in a system, power can be split and transmitted to several output shafts. This is commonly seen in automotive transmissions, where gear pulley systems allow power to be distributed to different gears for different speed ratios. In industrial machinery, multiple pulleys can be used to drive various conveyor belts or auxiliary equipment simultaneously. This power distribution capability enables gear pulleys to efficiently transmit power to multiple components within a system.
- Mechanical Advantage: Gear pulleys provide mechanical advantage in power transmission systems. The mechanical advantage is the ratio of output force (torque) to input force (torque). By utilizing gears or pulleys with different sizes, gear pulleys can amplify or reduce the mechanical advantage. This allows for the adaptation of power transmission to match the specific requirements of the driven component. Gear pulleys enable the transmission of high torque at low speeds or low torque at high speeds, depending on the mechanical advantage needed.
Overall, gear pulleys assist in the transmission of mechanical power by controlling speed, torque, and direction, distributing power to multiple components, and providing mechanical advantage. Their ability to manipulate these parameters makes gear pulleys versatile and valuable components in various mechanical systems across industries.


editor by CX
2024-05-15